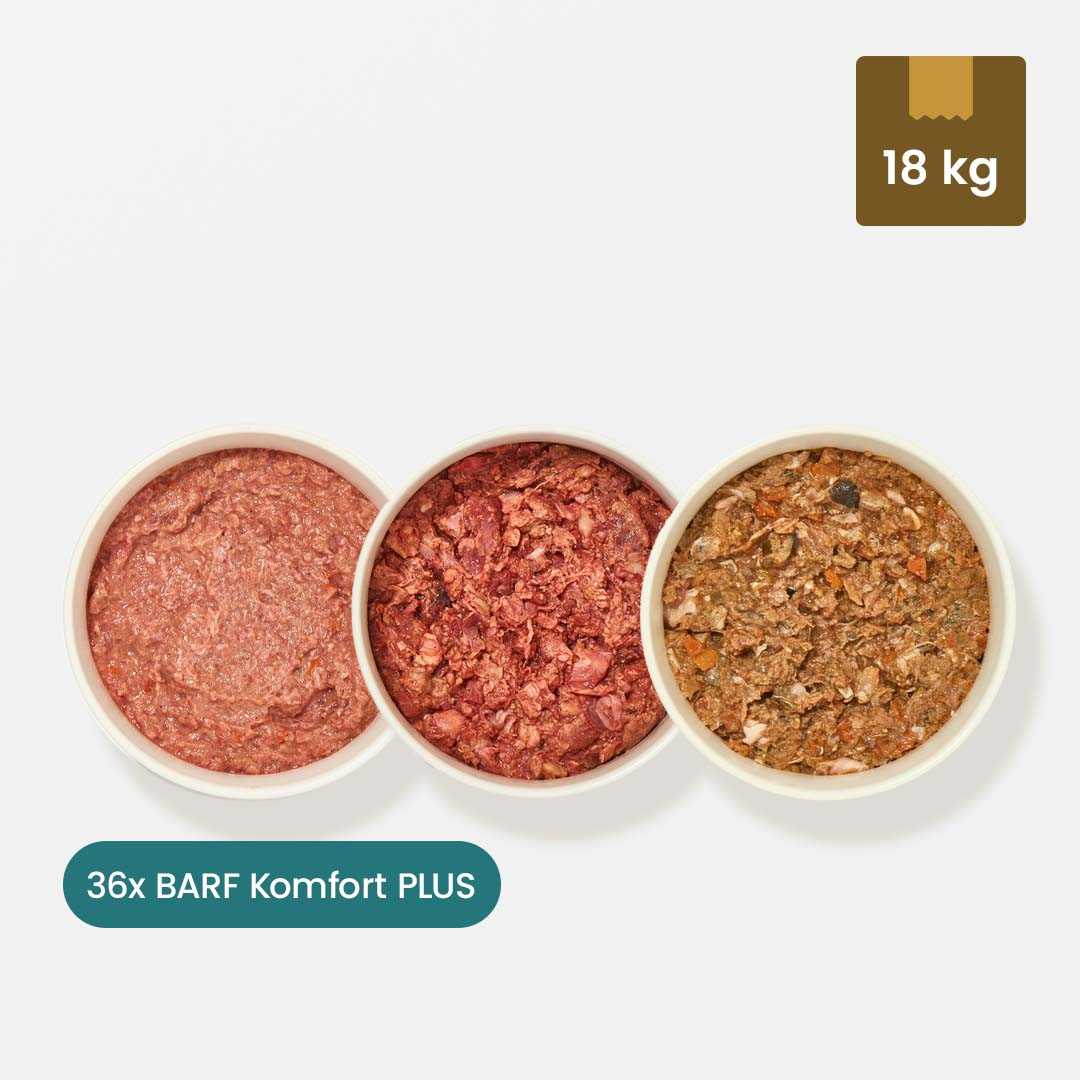
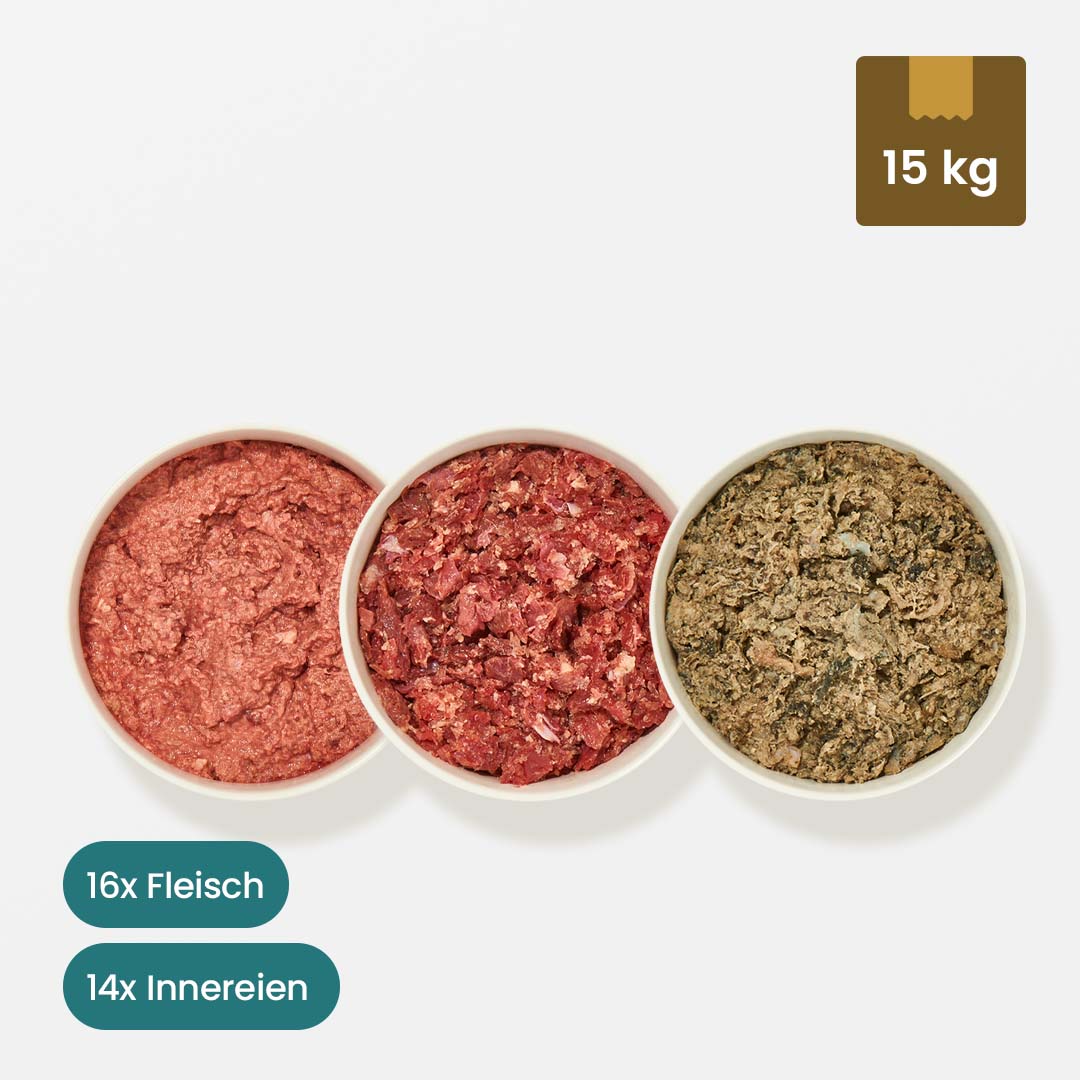
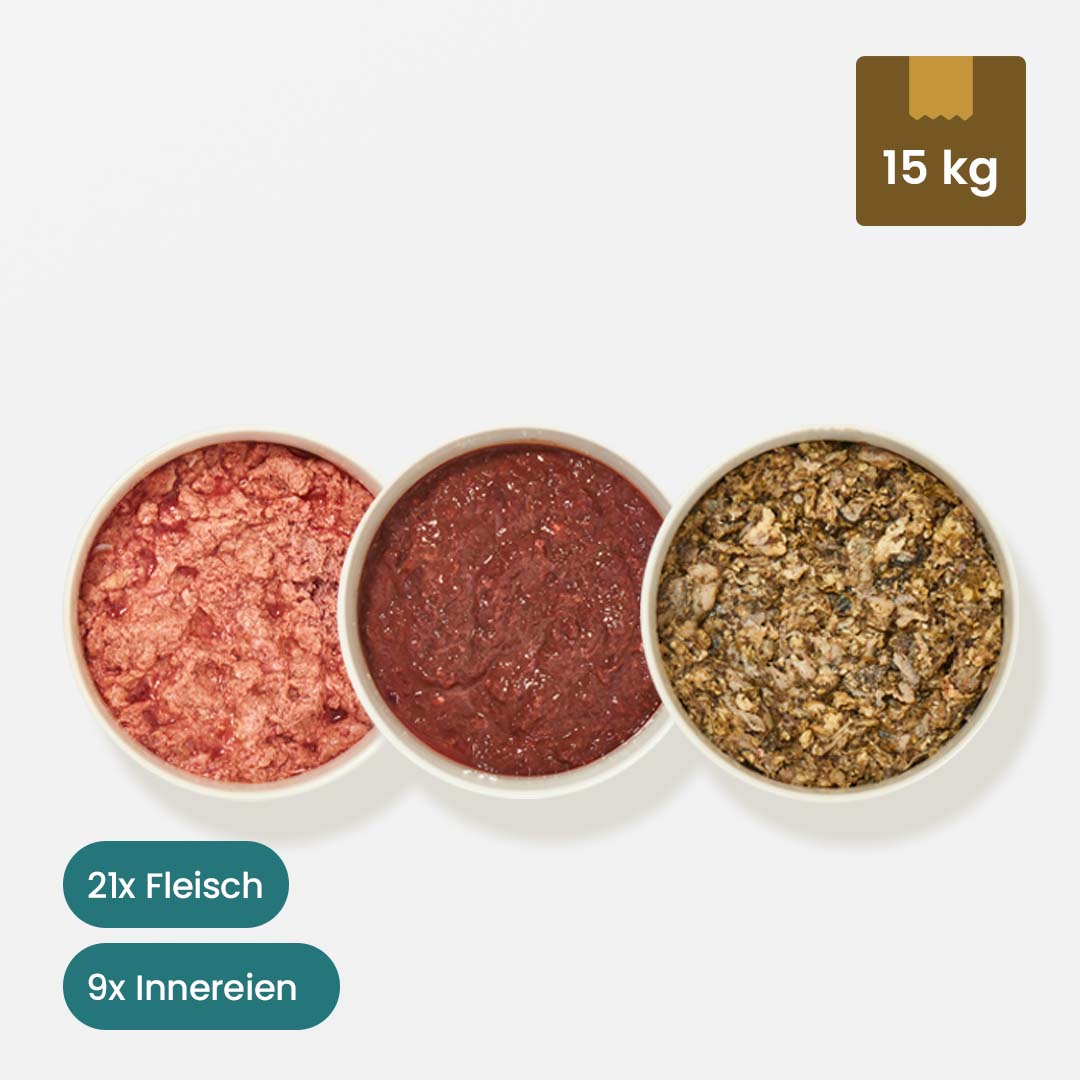
If you discover a sebaceous cyst on your dog, there is no reason to panic. With a sebaceous cyst (atheroma), your dog has a small lump or bump on the skin, which can have two different causes. A "true" atheroma occurs when epithelial tissue breaks off and collects with sebum in a small capsule. In this case, there is no outlet. The so-called "false" atheroma occurs when a sebaceous gland becomes blocked, so that the sebum that continues to be produced collects in a capsule at the gland outlet. This creates an outlet.
The sebaceous cyst usually feels firm and elastic on the dog, and its size can vary from the size of a small lentil to a chicken egg. It usually occurs on heavily hairy areas on the neck or back and is not painful. So if you come across a lump when stroking it and your four-legged friend hardly reacts to the touch, you may have found an atheroma. Your dog should still be taken to a veterinarian's office, as the lump could be a tumor or a disease and because bacteria collect on the sebaceous cyst, which can penetrate the skin. The veterinary staff usually removes the sebaceous cyst from the dog surgically. This only requires a short procedure. If the atheroma is discovered early, the prognosis for successful treatment is extremely good - and your dog can enjoy its BARF to the fullest again.