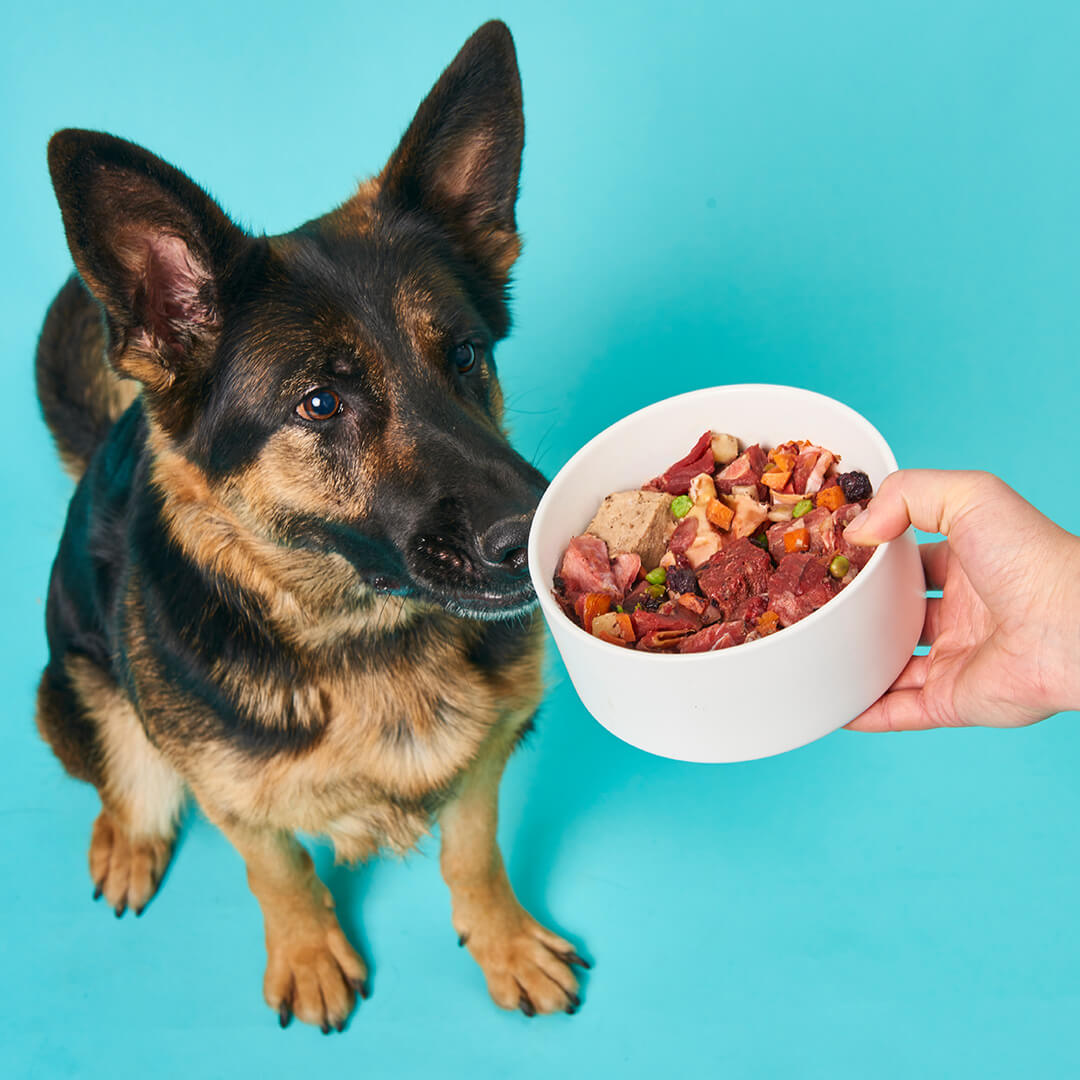
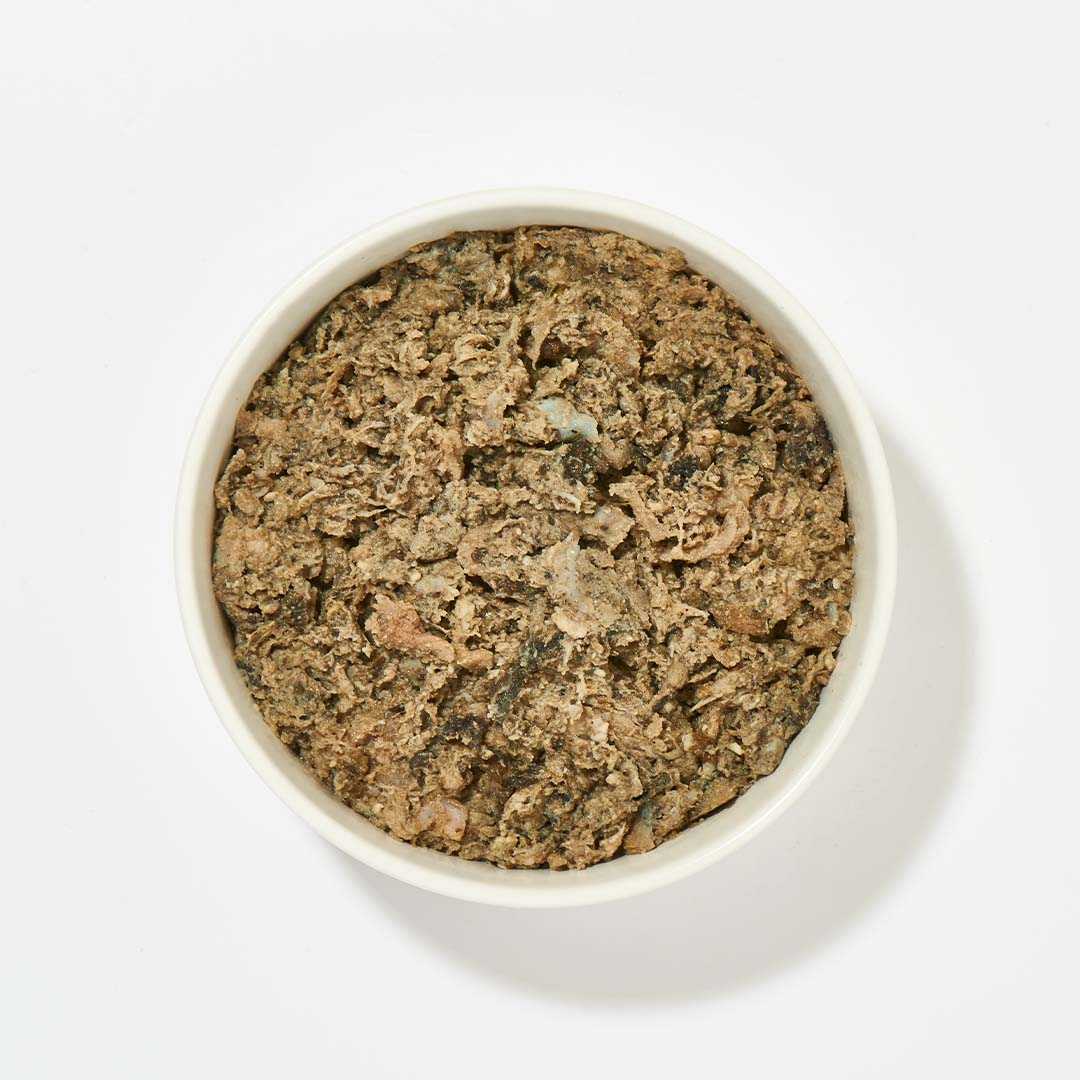
The sense of taste is less important for cats and dogs than for humans. While our four-legged friends can rely on their sense of smell in many respects, we perceive much more with our tongue. The reason for this is that the taste receptors are less developed in our beloved pets: In dogs, the sense of taste depends on 1,700 of these receptors, and in cats, on just 500. In contrast, humans have 9,000 taste receptors!
Can cats and dogs even taste? Given the small number of receptors, this question may well arise, but there is a clear answer: yes. In fact, dogs perceive the same tastes as humans. Dogs can therefore taste savory (meaty), sweet, sour, salty and bitter. However, dogs have very little sense of saltiness, as the generally high meat content means there is no real need to taste it. This is even more extreme with cats: as carnivores , they only eat meat and fish, and can taste a little salt, but nothing sweet. From an evolutionary perspective, it simply gave cats no advantage to distinguish between different sweeteners. On the other hand, dogs stumble across plant-based food more often, which is why it was an advantage for them if they could recognize ripe fruit, for example.
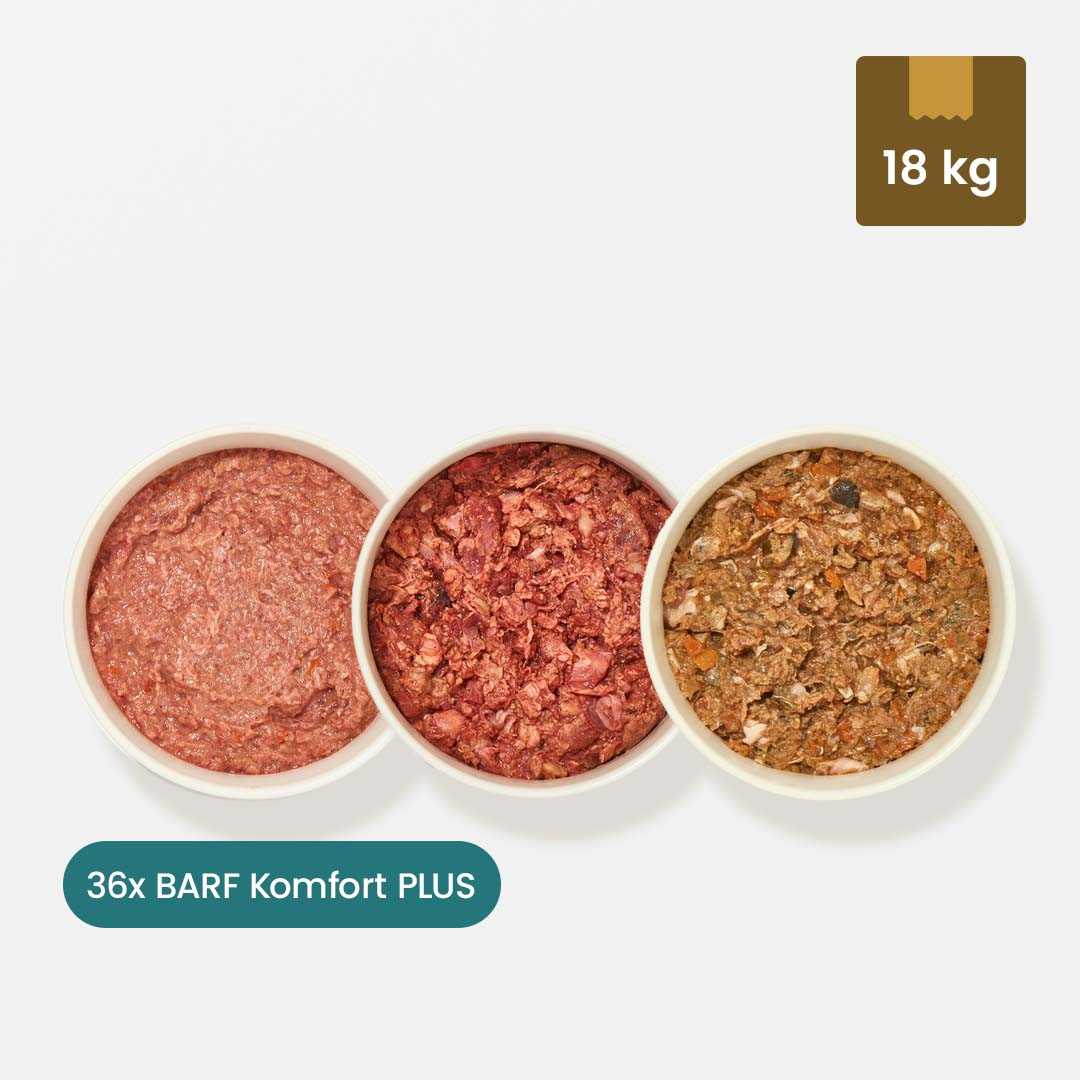
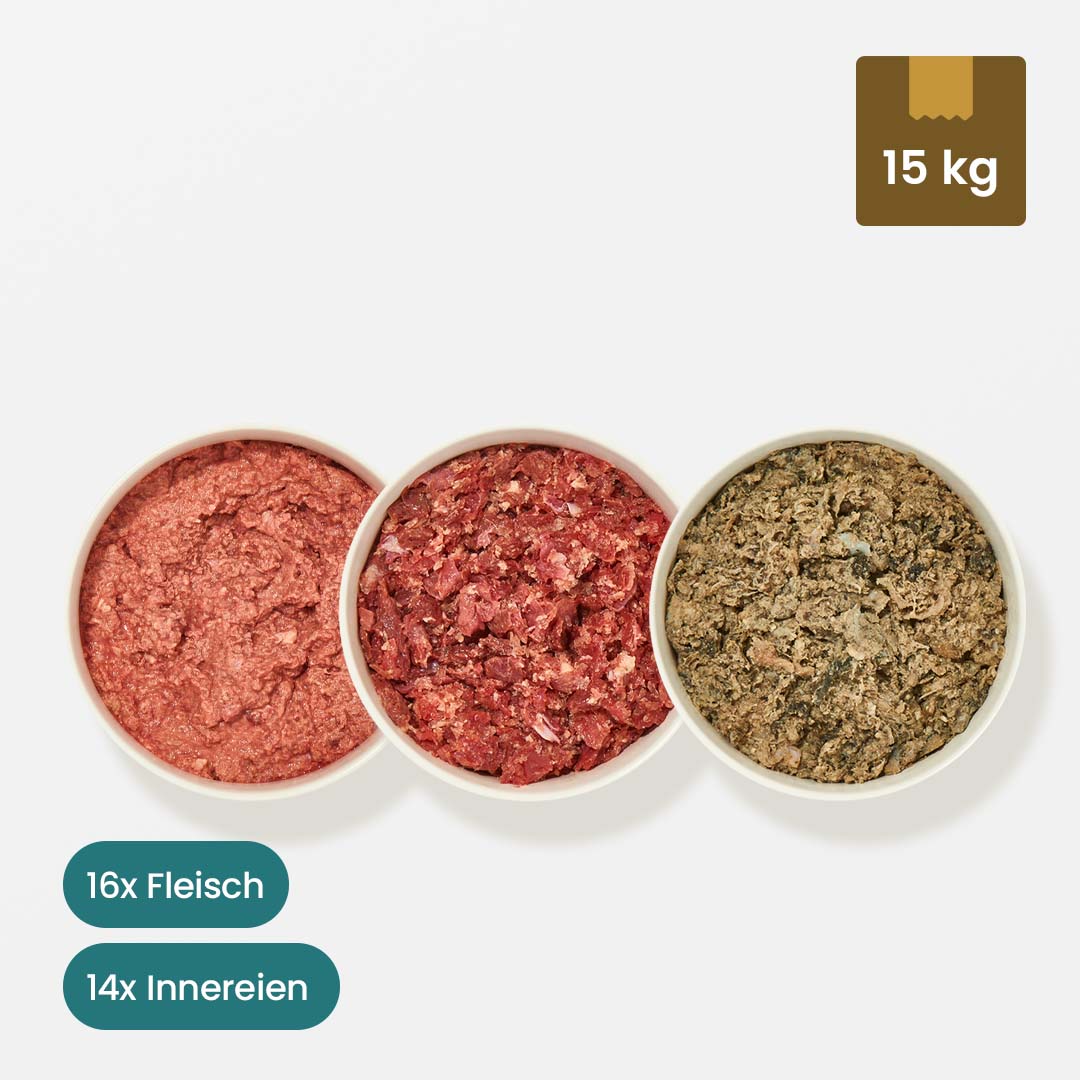
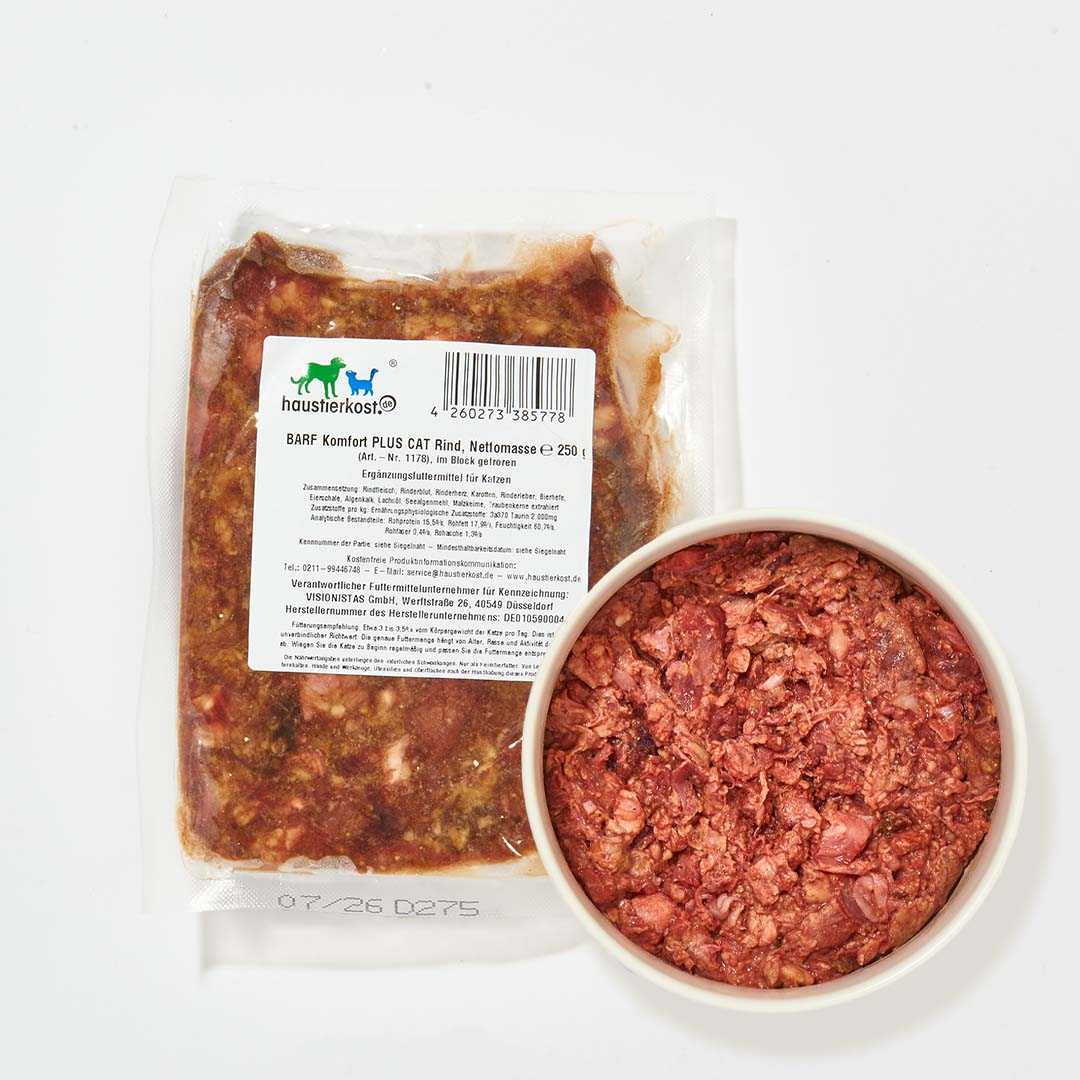
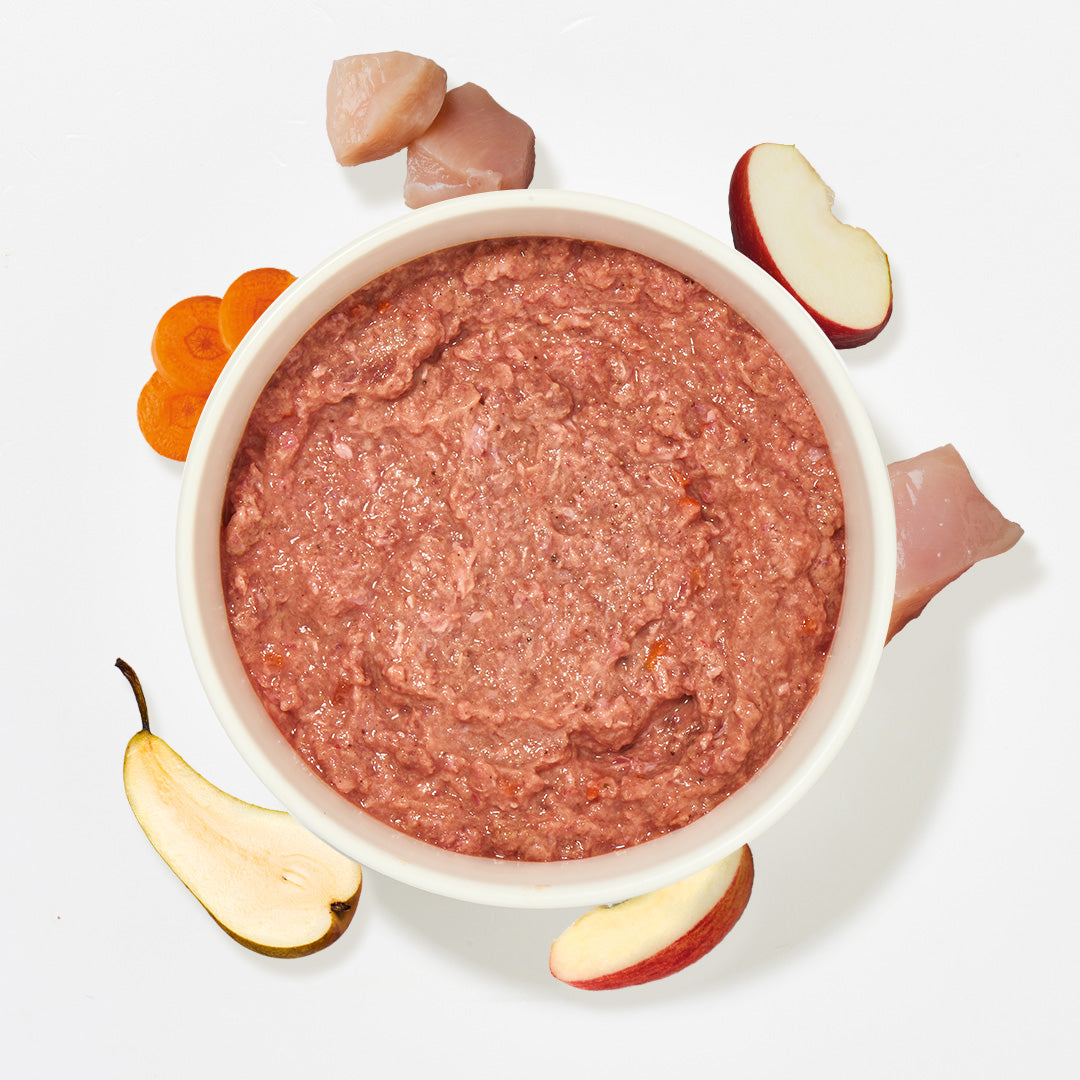
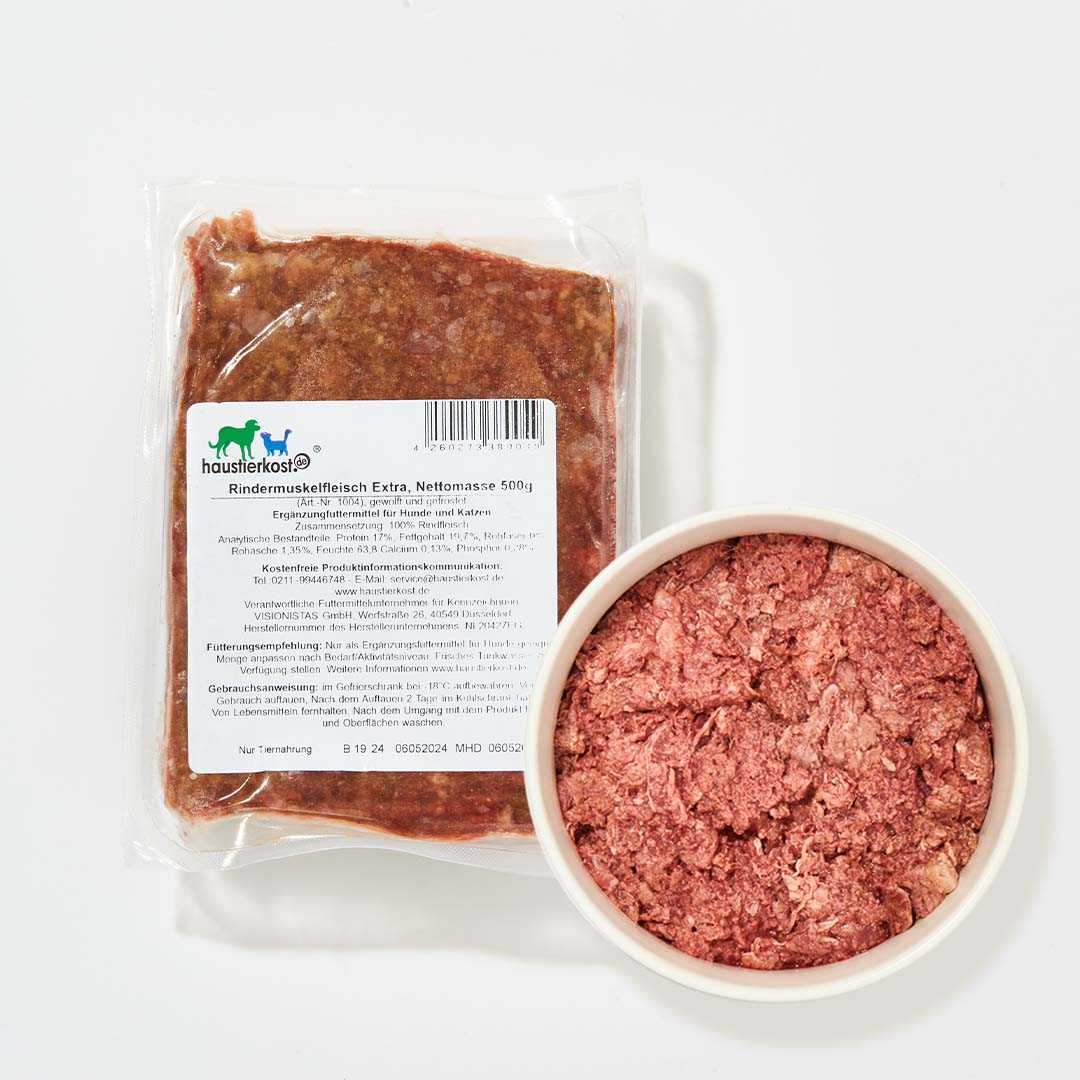
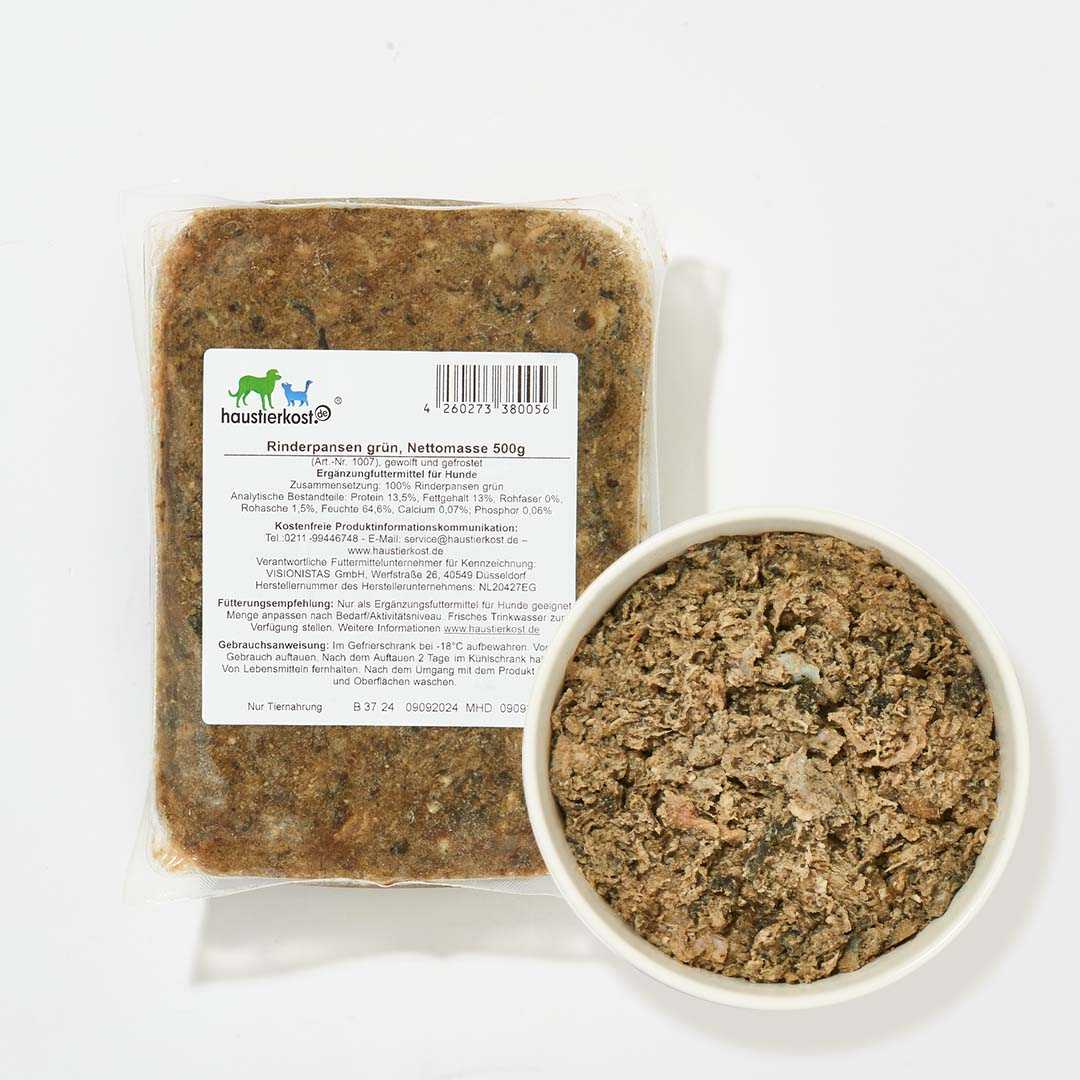
Of course, cats can also digest many types of fruit and vegetables, which is why they are used as a tasty source of vitamins in BARF . Discover our fruit and vegetables for cats as well as the numerous variations of BARF meat to fully appeal to the taste buds of cats and dogs.